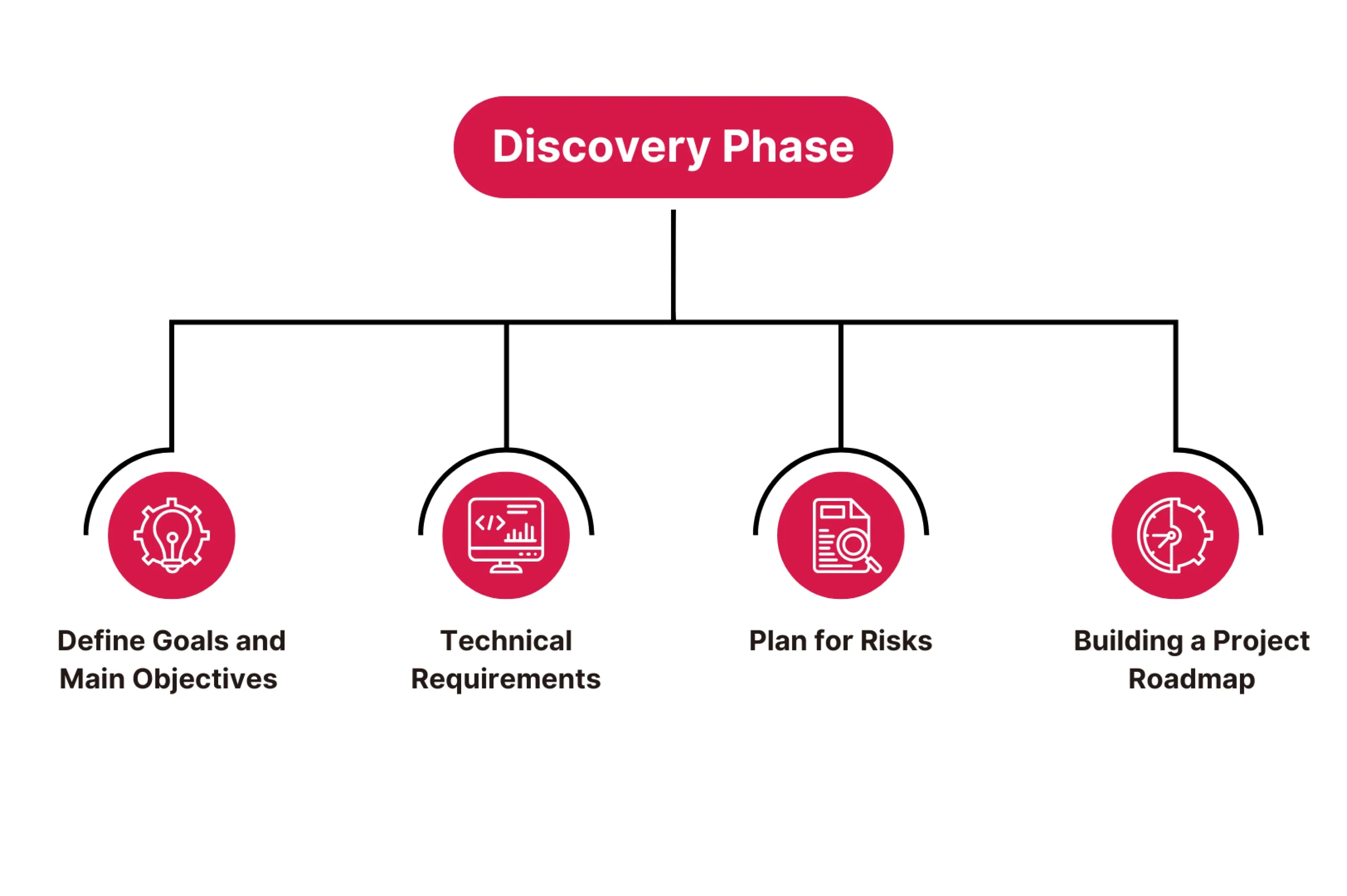
Why the Discovery Phase?
Have you ever been part of a project that started with big promises but just did not deliver in the end? More often than not, it is because the project skipped a proper Discovery phase.
Discovery is where you get clear on the “why” behind the project.
The discovery phase is where every project begins, collecting all the essential information, exploring ideas, getting to know the target market, and setting technical needs. This phase is also about defining the project’s scope and understanding what is required before jumping into development.
During Discovery, you look closer to get to the essence of the project by addressing some key questions:
- Why this project? Is this software really necessary, and if so, why?
- Who is going to use it? Are they professionals, students, everyday users, or experienced developers?
- How will it work? Do you have a solid idea of the features that will truly meet their needs?
Here we can also mention the Key Parts of the Discovery Phase:
- Project Goals and Objectives: Get clear on what the project is aiming to achieve so everyone’s on the same page.
- Understanding the Target Audience: Dive into who the end users are, their needs, and what they expect from the product.
- Technical Requirements: Lay out the technology, tools, and infrastructure you will need to bring the project to life.
- Risk Assessment: Spot any potential risks early and plan for how to menage them if they come up.
- Timeline and Key Phases: Create a timeline with important phases to keep the project moving forward smoothly.
- Resource Planning: Figure out the budget, tools, and team roles needed to get the project done right.
- Create Roadmap: This is the process of creating a complete plan of action that includes schedules, materials, project scope, and work organization.
Now let’s walk through each part of this phase, step-by-step, to see how it lays a solid foundation for your project’s success.
Discovery in Detail: Step-by-Step
Define Goals and Main Objectives
Every project has its own goal, but did u really understand it? They should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). The product goals often include: increasing user engagement, expanding market reach and the objective should be quantifiable, such as the number of new users.
So, upon that here comes the question: What problem is your software truly solving?
At this point is helpful to think about the project from different angles:
- User perspective: What does the software help users to do better, faster, or just easier?
- Business perspective: Does this software support the business's overall goals like reducing cost and improving efficiency?
Stakeholders Alignment
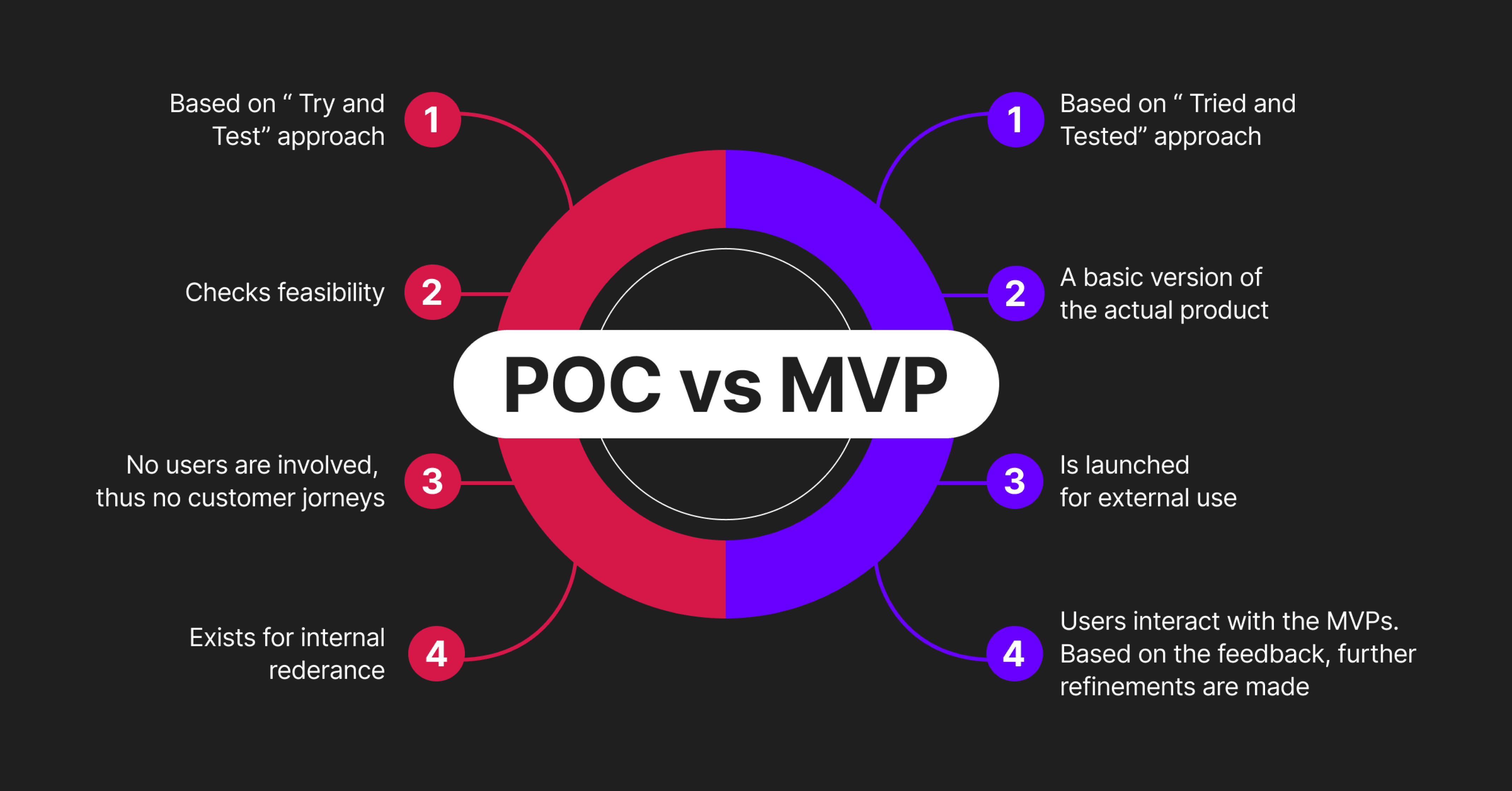
Getting stakeholders involved right from the start in the Discovery phase is key. These might be team members, clients, or department heads, each bringing their own valuable perspective. When you bring stakeholders in early during the Discovery phase for a proof of concept in software development, you get their insights right from the start. You set clear expectations and avoid misunderstandings down the road.
Ever been in a project where a key person joined too late, and suddenly, things went sideways? Involving stakeholders from day one keeps everyone on the same page and invested in making the project a success. It is about creating alignment, not just gathering feedback.
Understand End-Users
Now is the time to dig into who will be using this proof of value software and what they need. Talk to users, run surveys, and look at existing data. This helps you see their real preferences and challenges. And it is not just about knowing their age or job, it is about finding out what problems they face and how they currently solve them.
Think about it: When was the last time you talked directly with your users? The more you know about them, the better your chances of building proof of concept in software development that meets real needs and delivers real value.
Technical Requirements
Identify the technology, tools, and infrastructure needed to bring the project to life. This involves choosing software, programming languages, frameworks, and any essential hardware that supports development. It is also about understanding the technical limitations and scalability needs of the project.
By mapping out these requirements early, you create a solid technical foundation that helps avoid compatibility issues or tech-related delays later. This step ensures that your proof of concept in software development or proof of value software project is built on stable, future-proof technology.
 Define the Project Scope
Define the Project Scope
Once you have set your goals and know your users, it is time to define the project scope. This means deciding what is included in the project and what is not. Setting boundaries can feel limiting, but it keeps the project focused and stops it from growing out of control.
Here is a tip: think about what is absolutely necessary for version one and what can wait for future updates. Prioritizing “must-haves” over “nice-to-haves” keeps the project on track and helps you stay within budget.
Do a Reality Check
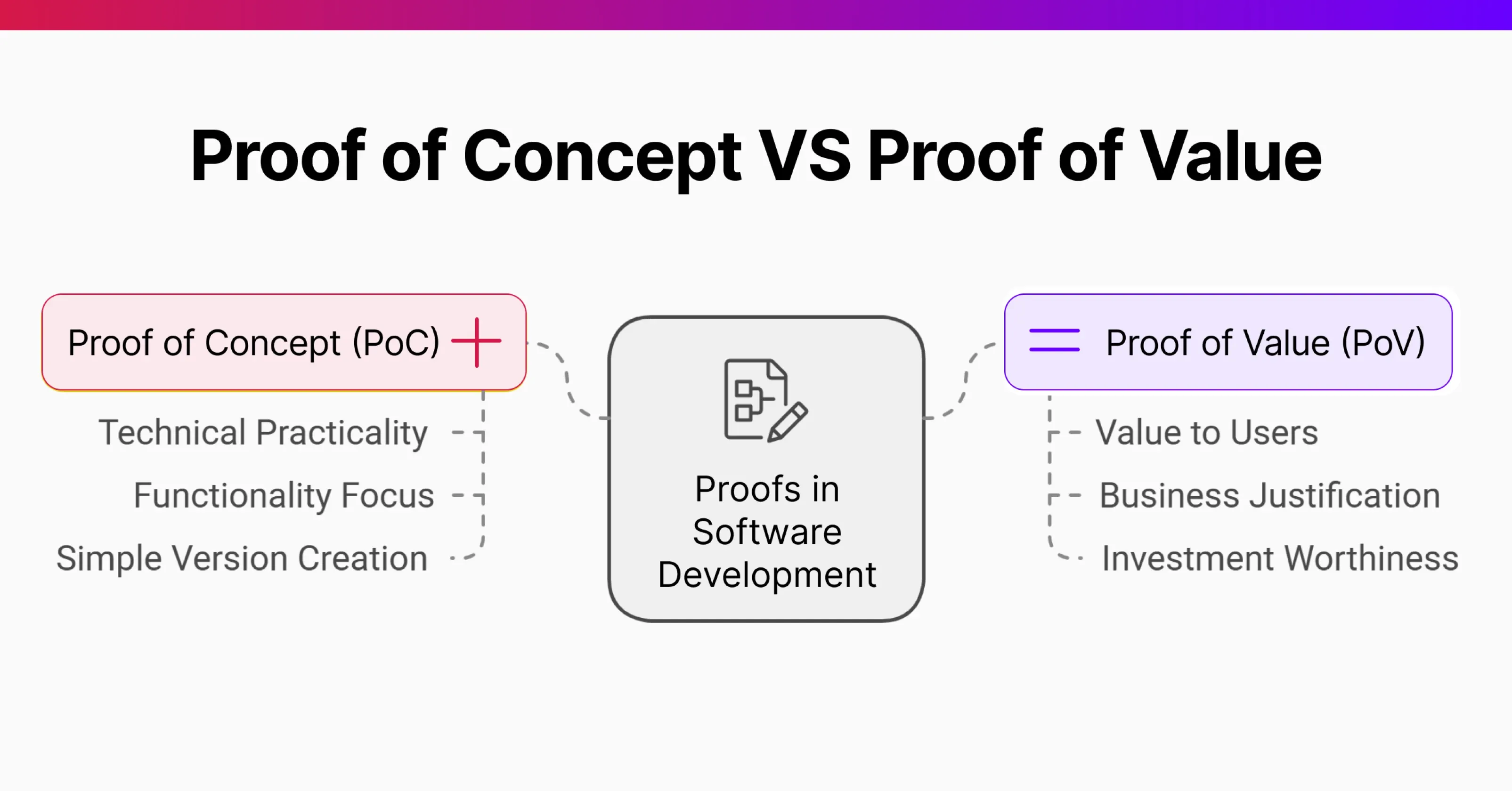
A reality check is all about making sure your goals and requirements are realistic given your resources, budget, and timeline. Start by asking: Is this project technically possible? Does our team have the skills needed to make it happen? This step confirms that you have got what it takes to bring your idea to life.
It is also important to think about market potential. Will people pay for this proof of value software? Are there similar products out there, and if so, how will yours stand out? A solid feasibility check now can save you from costly surprises later.
Plan for Risks
Every project comes with risks, but identifying them early allows you to resolve issues before they escalate. Common risks include things like budget limits, timeline delays, technical challenges, or unexpected challenges. Planning ahead helps reduce the likelihood of disruptions, so your project can keep moving forward.
When you identify risks early, your team can focus on solving problems rather than constantly putting out fires. This way, you are better equipped for any roadblocks that might pop up while building your proof of concept in software development.
Building a Project Roadmap
The project roadmap keeps everything on track. It breaks down each phase—design, development, testing, and launch—into clear steps with specific goals and deadlines. By assigning responsibilities, the roadmap makes sure everyone knows what they need to do and when to do it.
This roadmap is a flexible guide that gets updated as you go to keep up with any changes or new ideas that pop up. With this organized plan, your proof of concept in software development or proof of value software project stays focused and adaptable, keeping you on track from start to finish.
Why Skipping Discovery Can Cost You
Maybe you have asked yourself, yes the Discovery phase could be helpful but, what will happen if it is not included? Is that a sign that the project will fall out?
In this section, we will answer these questions and explore what can happen if Discovery is not part of the process. Without the discovery, projects can quickly run into harder problems, and more expensive to fix later. Imagine your project dealing with budget issues, missed deadlines, or a result that just does not fit what users want. Discovery helps you avoid that by setting a strong foundation. Here is how:
- Clear Goals: Discovery sets specific goals, so everyone knows what success looks like from the start.
- Understanding Your Audience: It is a chance to learn who your users are and build something that fits their needs.
- Noticing Risks Early: You will catch potential problems early and plan ahead to avoid surprises.
- Sticking to the plan: Discovery keeps everything organized and moving forward, with clear timelines and budgets.